C++小游戏——简单飞机大战(2)——代码与显示优化
0.前言
在上一篇中,我们在C++控制台中简单实现了飞机大战了逻辑,但是代码比较长,显示也不是很好看,这篇文章中,我们对上一篇的代码进行优化下,把很多过程封装成函数形式。让程序看上去更加精简。
一个合理化的游戏框架
1.游戏框架
框架参考:
int main() {
startup(); //数据初始化
while(1){ //游戏循环执行
show(); //显示画面
updateWithoutInput(); //与用户输入有关的更新
updateWithInput(); //与用户输入有关的更新
}
return 0;
}与输入无关的,比如敌机往下落,发射出去的子弹都不需要用户控制了。
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<conio.h>
using namespace std;
//全局变量定义
//数据初始化
void start(){
}
//显示画面
void show(){
}
//输入无关
void noInput(){
}
//输入有关
void Input(){
}
//主函数
int main(){
return 0;
} 2.飞机移动
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<conio.h>
#include<windows.h>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
//全局变量定义
int px,py; //飞机的坐标
int high, width; //画面的尺寸
//屏幕移动函数
void gotoxy(int x, int y) {
COORD pos = {x,y};
HANDLE hOut = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);// 获取标准输出设备句柄
SetConsoleCursorPosition(hOut, pos);//两个参数分别是指定哪个窗体,具体位置
}
//数据初始化
void start() {
high=64;
width=32;
px=high/3;
py=width/2;
}
//显示画面
void show() {
printf("★\n");
gotoxy(px+1,py+1);
printf("★\n");
gotoxy(px-1,py+1);
printf("★\n");
}
// 移动到控制台x,y坐标
//输入无关
void noInput() {
}
//输入有关
void Keydown() {
char input;
if (_kbhit()) { //如果有按键按下,则_kbhit()函数返回真
input = _getch();//使用_getch()函数获取按下的键值
switch(input) {
case 72: //上键
case 'w':
case 'W':
//px--; //for模式
py--; //gotoxy模式
break;
case 80: // 下键
case 's':
case 'S':
//px++;
py++;
break;
case 75: //左键
case 'a':
case 'A':
//py--;
px--;
break;
case 77: //右键
case 'd':
case 'D':
//py++;
px++;
break;
}
}
}
//主函数
int main() {
start(); //数据初始化
while(1){
Keydown();
system("cls");
gotoxy(px,py);
show();
}
return 0;
}3.构造子弹与子弹移动
这个地方的主要思路是子弹的坐标取飞机的坐标。当按下空格键时,子弹就会从飞机头部坐标发射出去。
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<conio.h>
#include<windows.h>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
//全局变量定义
int px,py; //飞机的坐标
int high, width; //画面的尺寸
int bullet_x,bullet_y; //子弹的位置
//屏幕移动函数
void gotoxy(int x, int y) {
COORD pos = {x,y};
HANDLE hOut = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);// 获取标准输出设备句柄
SetConsoleCursorPosition(hOut, pos);//两个参数分别是指定哪个窗体,具体位置
}
//数据初始化
void start() {
high=64;
width=32;
px=high/3; //飞机位置初始化
py=width/2; // 飞机位置
bullet_x=px; //子弹位置
bullet_y=py; // 子弹位置
}
//显示画面
void show() {
/*描绘飞机*/
printf("★\n");
gotoxy(px+1,py+1);
printf("★\n");
gotoxy(px-1,py+1);
printf("★\n");
/*描绘子弹*/
gotoxy(bullet_x,bullet_y-1);
printf("|\n");
}
// 移动到控制台x,y坐标
//输入无关
void noInput() {
}
//输入有关
void Keydown() {
char input;
if (_kbhit()) { //如果有按键按下,则_kbhit()函数返回真
input = _getch();//使用_getch()函数获取按下的键值
switch(input) {
case 72: //上键
case 'w':
case 'W':
//px--; //for模式
py--; //gotoxy模式
break;
case 80: // 下键
case 's':
case 'S':
//px++;
py++;
break;
case 75: //左键
case 'a':
case 'A':
//py--;
px--;
break;
case 77: //右键
case 'd':
case 'D':
//py++;
px++;
break;
case 32: //空格
bullet_y=py-1; //gotoxy模式下坐标变化
bullet_x=px;
break;
}
}
}
//主函数
int main() {
start(); //数据初始化
while(1){
Keydown();
system("cls");
gotoxy(px,py);
show();
}
return 0;
}上面这样做还是有个问题,就是子弹一旦发射出去,那么就不会受到飞机的控制,开始自己按照轨迹飞,所以应该把子弹的移动放到输入无关的部分。
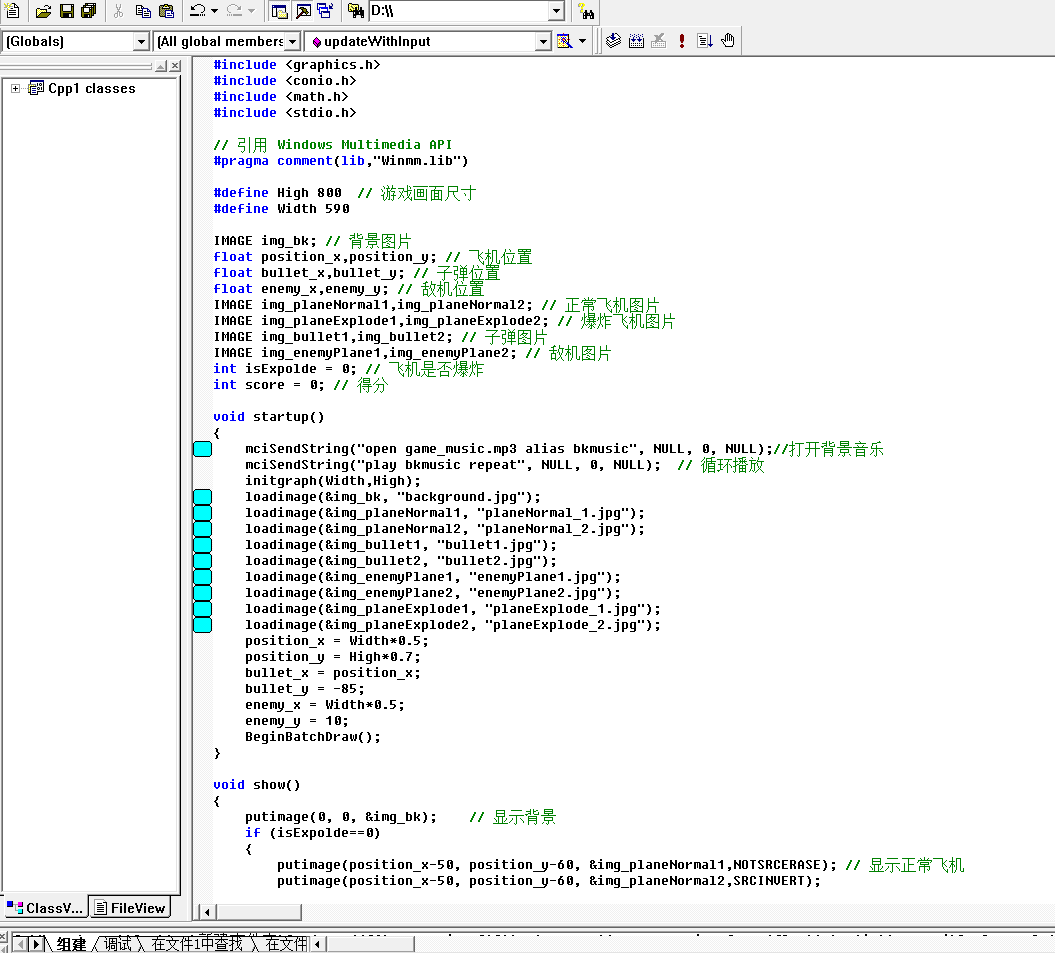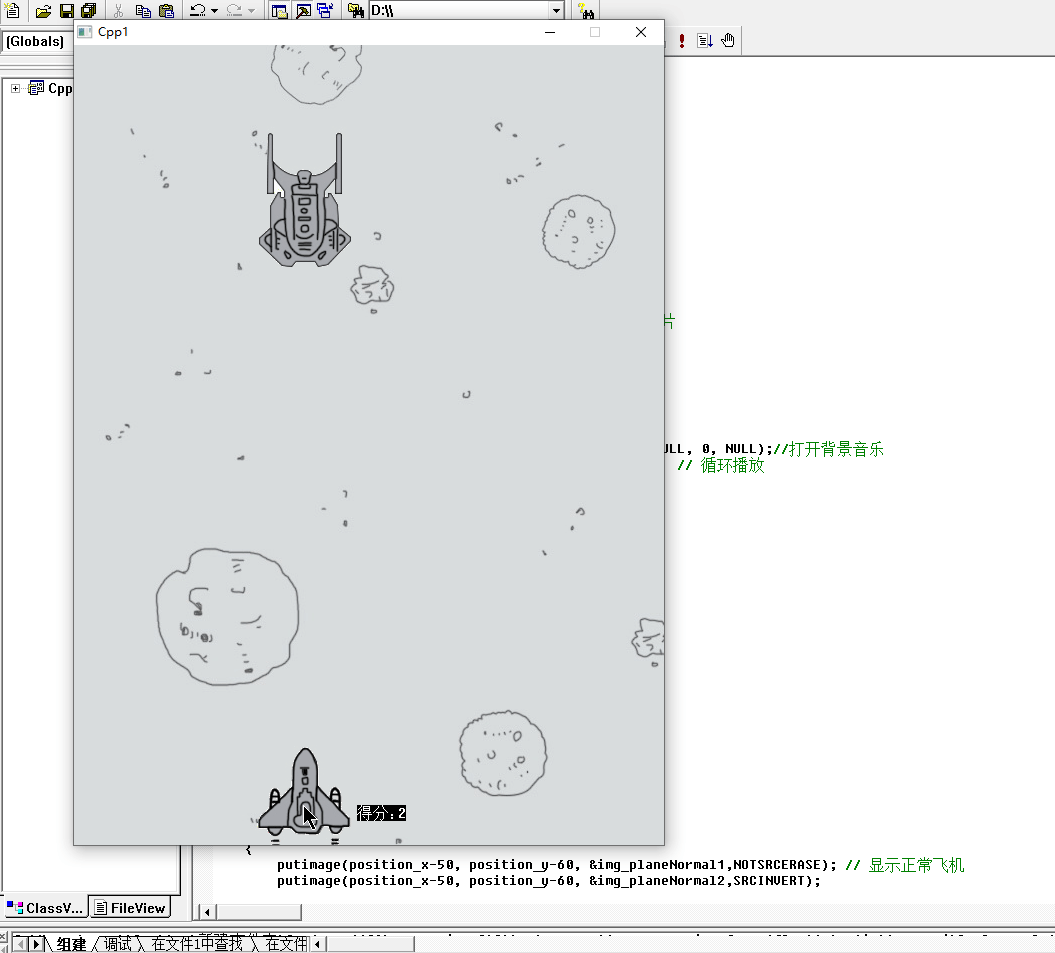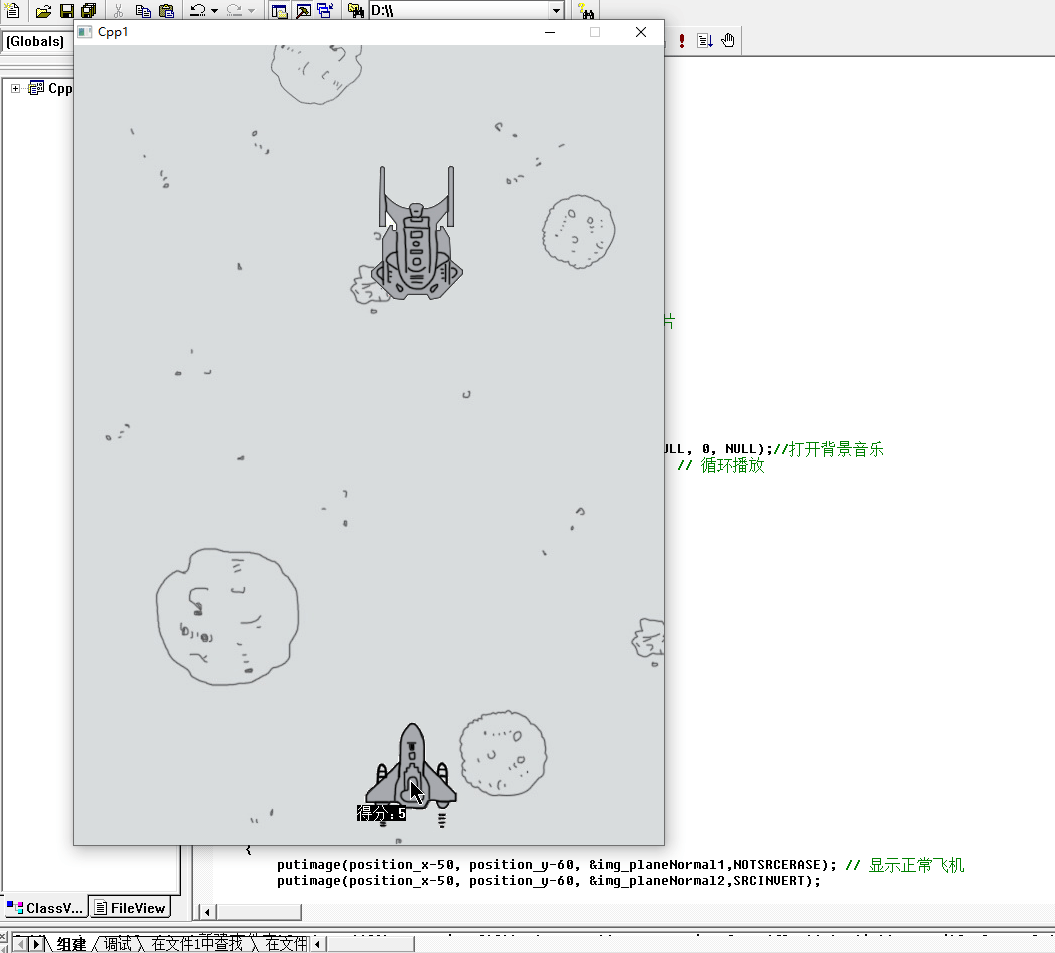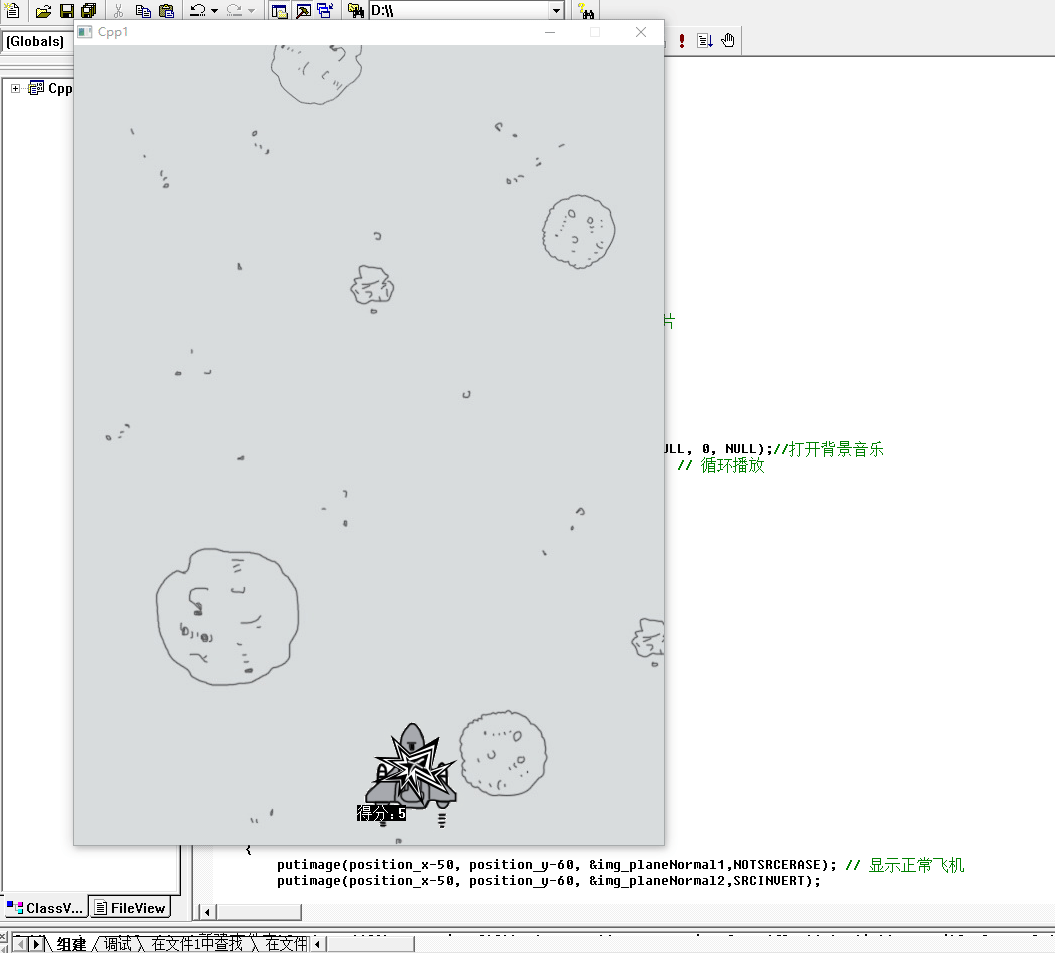
效果图:
这样基本实现了子弹和飞机脱离的情况,但是还有另外一个小BUG,就是游戏一开始子弹就自动发射了,我们可以让子弹的初始值为-1,这样就看不到了。
4.增加敌机
我们定义敌机的位置并初始化,同样的问题就是敌机的位置会往下落,那么敌机位置的变化也要放到输入无关的部分。
参考代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<conio.h>
#include<windows.h>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
//全局变量定义
int px,py; //飞机的坐标
int high, width; //画面的尺寸
int bullet_x,bullet_y; //子弹的位置
int enemy_x,enemy_y; //敌机位置
//屏幕移动函数
void gotoxy(int x, int y) {
COORD pos = {x,y};
HANDLE hOut = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);// 获取标准输出设备句柄
SetConsoleCursorPosition(hOut, pos);//两个参数分别是指定哪个窗体,具体位置
}
//数据初始化
void start() {
high=20;
width=30;
px=high/3; //飞机位置初始化
py=width/2; // 飞机位置
bullet_x=px; //子弹位置
//bullet_y=py; // 子弹位置
bullet_y=-1; // 子弹位置
enemy_x=px; //敌机位置
enemy_y=0; //敌机位置
}
//显示画面
void show() {
/*描绘飞机*/
printf("★\n");
gotoxy(px+1,py+1);
printf("★\n");
gotoxy(px-1,py+1);
printf("★\n");
/*描绘子弹*/
gotoxy(bullet_x,bullet_y-1);
printf("!\n");
/*描绘敌机*/
gotoxy(enemy_x,enemy_y);
printf("#\n");
}
// 移动到控制台x,y坐标
//输入无关
void noInput() {
/*子弹往上移动*/
if(bullet_y>-1)
bullet_y--;// 子弹往上移动
/*飞机往下移动*/
if(enemy_y<high)
enemy_y++;
else
enemy_y=0;
}
//输入有关
void Keydown() {
char input;
if (_kbhit()) { //如果有按键按下,则_kbhit()函数返回真
input = _getch();//使用_getch()函数获取按下的键值
switch(input) {
case 72: //上键
case 'w':
case 'W':
//px--; //for模式
py--; //gotoxy模式
break;
case 80: // 下键
case 's':
case 'S':
//px++;
py++;
break;
case 75: //左键
case 'a':
case 'A':
//py--;
px--;
break;
case 77: //右键
case 'd':
case 'D':
//py++;
px++;
break;
case 32: //空格
bullet_y=py-1; //gotoxy模式下坐标变化
bullet_x=px;
break;
}
}
}
//主函数
int main() {
start(); //数据初始化
while(1){
Keydown();
noInput();
system("cls");
gotoxy(px,py);
show();
}
return 0;
}问题又来了,敌机的位置总是固定的从一个位置下落,所以我们要加入随机数,让敌机在随机的位置生成,随机数一节参考“C++产生随机数”。
敌机如果飞行的太快,我们可以加上sleep函数。但是如果在主循环中加入sleep函数,会导致我们的飞机和敌人的飞机同时变慢(相当于没变)。那么我们有个思路是让敌机处于循环中,我们执行speed次,敌机才移动一次,这样就能达到我们移动速度不变,但是敌机移动变慢了的.
参考代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<conio.h>
#include<windows.h>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
//全局变量定义
int px,py; //飞机的坐标
int high, width; //画面的尺寸
int bullet_x,bullet_y; //子弹的位置
int enemy_x,enemy_y; //敌机位置
int speed; //延迟时间
//屏幕移动函数
void gotoxy(int x, int y) {
COORD pos = {x,y};
HANDLE hOut = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);// 获取标准输出设备句柄
SetConsoleCursorPosition(hOut, pos);//两个参数分别是指定哪个窗体,具体位置
}
//数据初始化
void start() {
high=20;
width=30;
px=high/3; //飞机位置初始化
py=width/2; // 飞机位置
bullet_x=px; //子弹位置
//bullet_y=py; // 子弹位置
bullet_y=-1; // 子弹位置
enemy_x=px; //敌机位置
enemy_y=0; //敌机位置
speed=2; //敌机移动速度
}
//显示画面
void show() {
/*描绘飞机*/
printf("★\n");
gotoxy(px+1,py+1);
printf("★\n");
gotoxy(px-1,py+1);
printf("★\n");
/*描绘子弹*/
gotoxy(bullet_x,bullet_y-1);
printf("!\n");
/*描绘敌机*/
gotoxy(enemy_x,enemy_y);
printf("#\n");
}
// 移动到控制台x,y坐标
//输入无关
void noInput() {
/*子弹往上移动*/
if(bullet_y>-1)
bullet_y--;
/*飞机往下移动*/
static int speed_tmp=0;
if(speed_tmp<speed)
speed_tmp++;
if(speed_tmp==speed) {
srand((int)time(NULL));
if(enemy_y<high){
enemy_y++;
speed_tmp=0; //速度重置
}
else {
enemy_y=0;
enemy_x=rand()%width;
}
}
}
//输入有关
void Keydown() {
char input;
if (_kbhit()) { //如果有按键按下,则_kbhit()函数返回真
input = _getch();//使用_getch()函数获取按下的键值
switch(input) {
case 72: //上键
case 'w':
case 'W':
//px--; //for模式
py--; //gotoxy模式
break;
case 80: // 下键
case 's':
case 'S':
//px++;
py++;
break;
case 75: //左键
case 'a':
case 'A':
//py--;
px--;
break;
case 77: //右键
case 'd':
case 'D':
//py++;
px++;
break;
case 32: //空格
bullet_y=py-1; //gotoxy模式下坐标变化
bullet_x=px;
break;
}
}
}
//主函数
int main() {
start(); //数据初始化
while(1) {
Keydown();
noInput();
system("cls");
gotoxy(px,py);
show();
}
return 0;
}效果图
5.击中敌机
击中敌机的思路是子弹的坐标和飞机的坐标相等就是击中敌机了,但是击中之后要记得把子弹消失,然后敌机要继续随机生成。同时加上得分效果。
效果:
6.最终代码
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<conio.h>
#include<windows.h>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
//全局变量定义
int px,py; //飞机的坐标
int high, width; //画面的尺寸
int bullet_x,bullet_y; //子弹的位置
int enemy_x,enemy_y; //敌机位置
int speed; //敌机速度
int score; //用户得分
//屏幕移动函数
void gotoxy(int x, int y) {
COORD pos = {x,y};
HANDLE hOut = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);// 获取标准输出设备句柄
SetConsoleCursorPosition(hOut, pos);//两个参数分别是指定哪个窗体,具体位置
}
//数据初始化
void start() {
high=20;
width=30;
px=high/3; //飞机位置初始化
py=width/2; // 飞机位置
bullet_x=px; //子弹位置
//bullet_y=py; // 子弹位置
bullet_y=-1; // 子弹位置
enemy_x=px; //敌机位置
enemy_y=0; //敌机位置
speed=4; //敌机移动速度
}
//显示画面
void show() {
/*描绘飞机*/
printf("★\n");
gotoxy(px+1,py+1);
printf("★\n");
gotoxy(px-1,py+1);
printf("★\n");
/*描绘子弹*/
gotoxy(bullet_x,bullet_y-1);
printf("!\n");
/*描绘敌机*/
gotoxy(enemy_x,enemy_y);
printf("#\n");
/*展示得分*/
gotoxy(high,width);
printf("得分:%d",score);
}
// 移动到控制台x,y坐标
//输入无关
void noInput() {
/*子弹往上移动*/
if(bullet_y>-1)
bullet_y--;
/*飞机往下移动*/
static int speed_tmp=0;
if(speed_tmp<speed)
speed_tmp++;
if(speed_tmp==speed) {
srand((int)time(NULL));
if(enemy_y<high){
enemy_y++;
speed_tmp=0; //速度重置
}
else {
enemy_y=0;
enemy_x=rand()%width;
}
}
/*判断击中敌机*/
if(enemy_x==bullet_x && enemy_y==bullet_y)
{
score++;
bullet_y=bullet_x=-1; //子弹消失
enemy_y=0;
enemy_x=rand()%width; //敌机继续生成
}
}
//输入有关
void Keydown() {
char input;
if (_kbhit()) { //如果有按键按下,则_kbhit()函数返回真
input = _getch();//使用_getch()函数获取按下的键值
switch(input) {
case 72: //上键
case 'w':
case 'W':
//px--; //for模式
py--; //gotoxy模式
break;
case 80: // 下键
case 's':
case 'S':
//px++;
py++;
break;
case 75: //左键
case 'a':
case 'A':
//py--;
px--;
break;
case 77: //右键
case 'd':
case 'D':
//py++;
px++;
break;
case 32: //空格
bullet_y=py-1; //gotoxy模式下坐标变化
bullet_x=px;
break;
}
}
}
void HideCursor(){
CONSOLE_CURSOR_INFO cursor_info={1,0}; //第二个值表示隐藏光标
SetConsoleCursorInfo(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE),&cursor_info);
}
//主函数
int main() {
start(); //数据初始化
HideCursor(); //隐藏光标
while(1) {
Keydown();
noInput();
system("cls");
//gotoxy(0,0)
gotoxy(px,py);
show();
}
return 0;
}7.不足之处
显示BUG,左侧有个子弹
敌机不能击中玩家
显示频率过高
扫描二维码推送至手机访问。
版权声明:本文由青少年编程知识记录发布,如需转载请注明出处。